Remote work continues to thrive, and so does the need to understand tax responsibilities. Self-employed individuals and small business owners can benefit from various tax deductions that lower their taxable income. Many of these deductions originated under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), with some provisions currently set to expire in 2025, making it crucial to stay informed.
Table of Contents
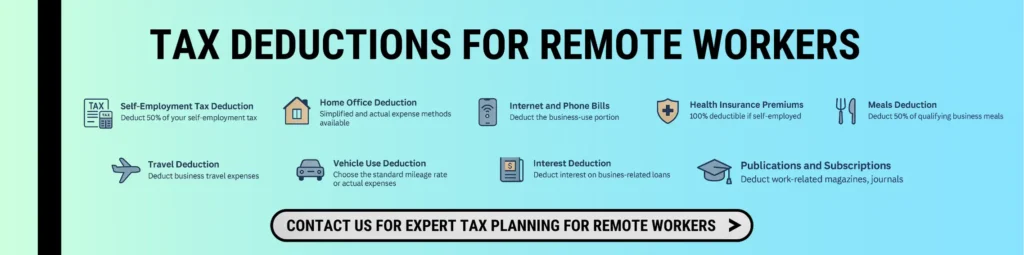
Here are the 10 most valuable tax deductions to consider in 2025 if you work from home.
1. Self-Employment Tax Deduction
Self-employed individuals are required to pay both the employer and employee shares of Social Security and Medicare, amounting to a combined total of 15.3%. However, you can deduct the employer-equivalent portion (7.65%) on your tax return.
Tip: If your income (combined with your spouse’s) exceeds $250,000, you may be subject to an additional 0.9% Medicare tax.
2. Home Office Deduction
If you regularly and exclusively use part of your home for business, you may qualify for this deduction. You can calculate it using:
- Simplified Method: $5 for each square foot, with a maximum of 300 square feet.
- Actual Expense Method: Based on the business-use percentage of actual expenses like utilities, insurance, and depreciation
3. Internet & Phone Bill Dedication
You can deduct the business-use portion of your internet and phone services. This applies whether or not you claim the home office deduction.
- Deduct long-distance or second-line business calls.
- Prorate your internet bill for business use.
4. Health Insurance Premium Dedication
If you’re self-employed and pay for your health insurance, you may deduct 100% of premiums for yourself, your spouse, dependents, and children under age 27.
Use the IRS’s Self-Employed Health Insurance Deduction Worksheet in Publication 535 for accuracy.
5. Meals Deduction
In 2025, meals with clients or while traveling for business will be 50% deductible. Keep detailed records of the business purpose for each meal.
The temporary 100% deduction for restaurant meals expired after 2022.
6. Travel Expense Deduction
Business trips that include overnight stays and business activities outside your tax home qualify as deductible travel.
Allowable expenses:
- Transportation
- Lodging
- Meals (50%)
Tip: Maintain records of meetings, events, and business objectives for each trip.
7. Vehicle Use Dedication
Use your vehicle for work? Deduct using either:
- Standard Mileage Rate (check the IRS rate for 2025)
- Actual Expenses (fuel, repairs, maintenance, insurance)
Keep a logbook noting business mileage, dates, and trip purposes.
8. Interest on Business Loans
Interest paid on business-related loans or credit cards is deductible, provided the funds are used for business expenses. Personal purchases are not eligible.
9. Publications & Subscriptions
Subscriptions to industry-specific materials and professional journals are deductible if directly related to your business.
Example: A personal trainer subscribing to Fitness Business Insider or a marketing pro buying a digital advertising playbook.
10. Educational Expenses
Courses or training that maintain or enhance your business skills are deductible.
Examples:
- Tax pro taking advanced compliance training
- Designer learning new software used in the current client work
Education must be relevant to your current business, not for a new career.
Final Thoughts
Understanding and applying these deductions can significantly lower your tax liability. Considering that TCJA provisions may end in 2025, it’s essential to assess your financial strategy now and take advantage of available opportunities.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can I write off my home office on my taxes in 2025?
Yes, if you use part of your home regularly and exclusively for business, you can claim the home office deduction using either the simplified or actual expense method.
2. What percentage of internet can I deduct if I work from home?
You can deduct the business-use percentage of your internet bill. Keep a reasonable estimate or documentation of usage to support the deduction.
3. Are meals still 100% deductible for remote workers in 2025?
No. The temporary 100% deduction expired. In 2025, only 50% of business meals are deductible, including those during travel or with clients.
4. Can I deduct mileage if I use my car for work from home?
Yes, if you drive for business purposes (e.g., to meet clients), you can deduct using the standard mileage rate or actual expenses. Keep a mileage log.
5. What business education expenses are tax deductible?
Education that maintains or improves skills for your current business is deductible. It must be relevant and not intended for a new career.










